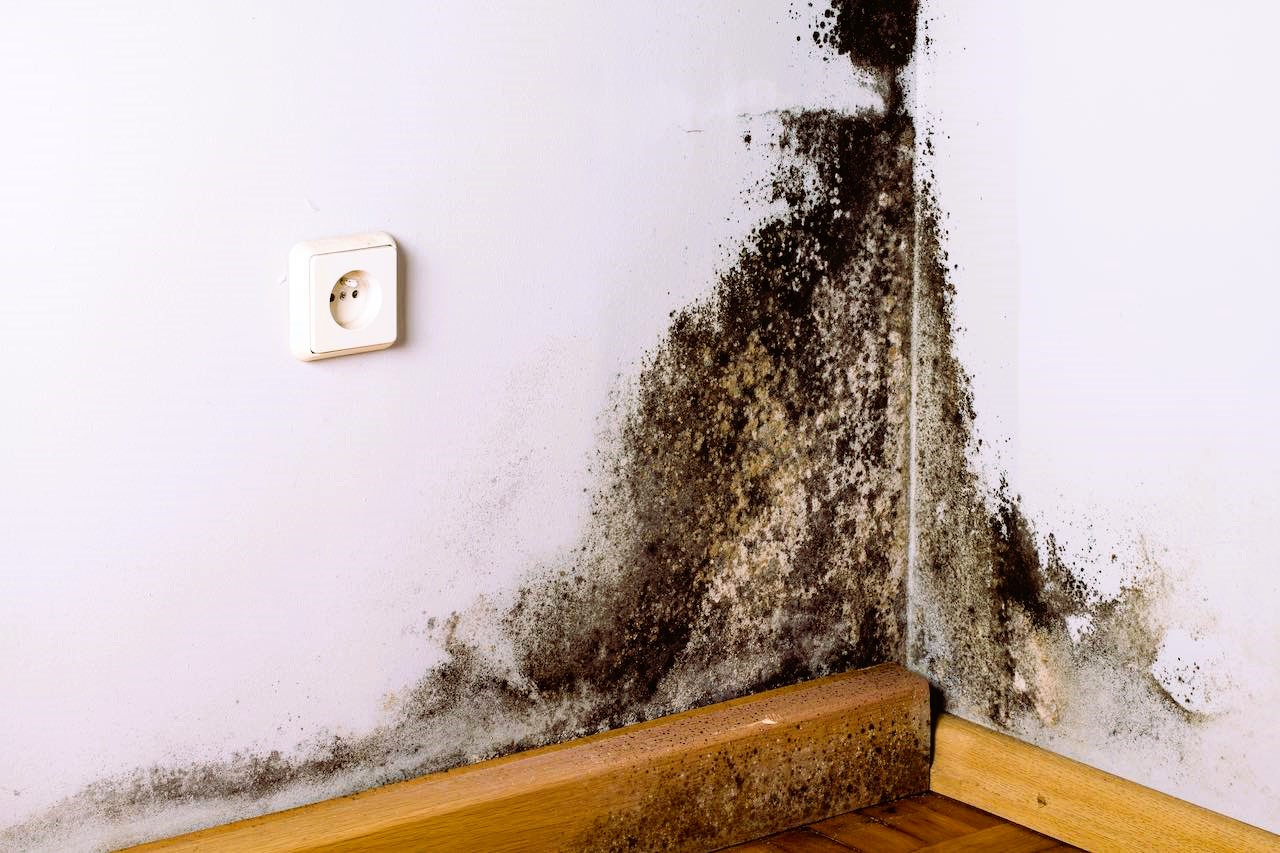
Black mold, scientifically known as Stachybotrys chartarum, is a type of mold that has garnered attention due to its potential health risks and the challenges associated with its identification and removal. While mold is a common occurrence in indoor and outdoor environments, black mold is of particular concern due to the mycotoxins it can produce. In this article, we will delve into the risks associated with black mold, methods for identification, and safe removal practices to create healthier living environments.
Risks of Black Mold Exposure:
Exposure to black mold and its mycotoxins can pose various health risks, especially when individuals have prolonged or intense contact with contaminated environments. Common health effects associated with black mold exposure include:
- Respiratory Issues: Black mold inhalation can lead to respiratory problems such as coughing, wheezing, throat irritation, and nasal congestion. Individuals with pre-existing respiratory conditions may experience more severe symptoms.
- Allergic Reactions: Black mold is a potent allergen, and exposure can trigger allergic reactions in sensitive individuals. Symptoms may include sneezing, runny or stuffy nose, itchy or watery eyes, and skin rashes.
- Headaches and Fatigue: Prolonged exposure to black mold may result in persistent headaches and fatigue. These symptoms can impact overall well-being and daily activities.
- Neurological Symptoms: Some studies suggest a potential link between black mold exposure and neurological symptoms, including difficulty concentrating, memory loss, and confusion. However, more research is needed to establish a clear connection.
Identification of Black Mold:
Identifying black mold can be challenging because it often appears similar to other molds, and not all molds that are black in color are Stachybotrys chartarum. Here are key characteristics to look for when identifying black mold:
- Color: While the name suggests black mold, it can also appear greenish-black or dark green. The color is not a definitive identification factor, as other molds may also exhibit similar hues.
- Texture: Black mold typically has a slimy or wet texture, making it distinct from other dry or powdery molds. The sliminess is due to the mycotoxins it produces.
- Location: Black mold thrives in areas with high humidity and moisture. It is commonly found in damp or water-damaged buildings, such as those affected by leaks, flooding, or inadequate ventilation.
- Smell: Black mold often has a musty odor, which can be a clue to its presence. However, relying solely on odor is not a reliable identification method, as many molds produce musty smells.

Safe Removal Practices:
Black mold removal should be approached with caution to minimize the risk of exposure and ensure the safety of individuals involved. Here are key steps for safe black mold removal:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Prioritize safety by wearing appropriate PPE, including an N95 respirator, goggles, gloves, and a protective suit. This helps prevent inhalation and skin contact with mold and its spores. To find mold on window shades and blinds, read our cleanroom guide.
- Isolation: Isolate the affected area to prevent the spread of mold spores to other parts of the building. Close off doors and windows and consider using plastic sheeting to contain the area.
- Moisture Control: Address the source of moisture to prevent the recurrence of mold growth. Fix leaks, improve ventilation, and reduce humidity levels in the affected area.
- HEPA Filtration: Use High-Efficiency Particulate Air (HEPA) filters in air purifiers and vacuums to capture airborne mold spores during the removal process.
- Cleaning Agents: Choose eco-friendly and biodegradable cleaning agents for mold removal. Solutions like vinegar, hydrogen peroxide, or baking soda can effectively clean surfaces without introducing harsh chemicals.
- Safe Disposal: Dispose of contaminated materials properly. Seal materials in heavy-duty plastic bags and follow local regulations for the disposal of mold-contaminated waste.
For comprehensive information on black mold, including risks, identification, and removal standards, refer to reputable sources such as Canada.ca for specific regional standards and recommendations.
Understanding the risks associated with black mold, identifying its presence, and implementing safe removal practices are essential steps in creating healthier indoor environments. By prioritizing safety, using eco-friendly cleaning agents, and adhering to established standards, individuals can effectively address black mold issues while minimizing the impact on human health and the environment. Regular inspections, moisture control measures, and prompt remediation are key components of a proactive approach to mold management. As we strive for healthier living spaces, incorporating safe and sustainable practices in black mold remediation is a vital aspect of overall well-being.